Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ikeura, Hiromi*; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 58(SI), p.SIIC04_1 - SIIC04_4, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)The electronic structure of the unoccupied conduction band of polycrystalline chloroaluminum phthalocyanine was investigated by X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) near the Cl K-edge. XAS spectra were recorded in total electron yield (TEY) and partial Auger electron yield (AEY) modes. Partial AEY spectra were measured using normal and spectator Cl KL L
L Auger yields as a function of photon energy. Although the TEY spectrum showed a broad shape; that was difficult to deconvolute curve fitting, the normal and spectator AEY spectra clearly showed that
Auger yields as a function of photon energy. Although the TEY spectrum showed a broad shape; that was difficult to deconvolute curve fitting, the normal and spectator AEY spectra clearly showed that 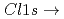
 *(Cl-Al) transition splits into two competitive peaks attributed to the core excitons (localized with a core hole) and conduction band (delocalized without a core hole). The existence of a band-like peak in the Cl K-edge XAS is evidence that the Cl axial ligand participates in forming the conduction band. Thus, band-like electron transport is expected to occur in the oligomer-like (-Al-Cl-Al-) site.
*(Cl-Al) transition splits into two competitive peaks attributed to the core excitons (localized with a core hole) and conduction band (delocalized without a core hole). The existence of a band-like peak in the Cl K-edge XAS is evidence that the Cl axial ligand participates in forming the conduction band. Thus, band-like electron transport is expected to occur in the oligomer-like (-Al-Cl-Al-) site.
Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
After the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in 2011, decontamination of radioactive cesium is a major concern for recovering from the environmental damage. It is generally known that Cs is irreversibly incorporated into clay minerals such as weathered biotite. Therefore, the development of efficient way to remove Cs has motivated research into understanding Cs adsorption and its physicochemical properties. Synchrotron radiation photoemission electron microscope (SR-PEEM) was applied to perform the pinpoint analysis of micrometer-sized weathered biotite particles with artificially adsorbed Cs. Spatial distributions of constituent elements were observed with nanometer resolution. Spatially resolved X-ray absorption spectra of the Cs M- and Fe L-edges were measured to determine the chemical states of each atom. The results demonstrate the utility of SR-PEEM as a tool for nanoscale chemical analyses of various environmental substances.
Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yano, Masahiro; Uozumi, Yuki*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Suzuki, Shinichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
The isotope separation of cesium-135 ( Cs), 2.3 million years lived nuclides in fission products, is an important issue for the transmutation annihilation. We are developing Cs selective carbon storage materials in order to avoid collision induced reverse isotope exchange of
Cs), 2.3 million years lived nuclides in fission products, is an important issue for the transmutation annihilation. We are developing Cs selective carbon storage materials in order to avoid collision induced reverse isotope exchange of  Cs atoms and
Cs atoms and  CsI molecules. We have investigated depth concentration distributions of Cs atom or CsI in C
CsI molecules. We have investigated depth concentration distributions of Cs atom or CsI in C as an absorbent material using electron emission angle-resolved, photon-energy dependent, and Ar
as an absorbent material using electron emission angle-resolved, photon-energy dependent, and Ar -sputtering time dependent X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) with synchrotron-radiation. Photon energy dependent XPS of a saturated amount of Cs doped on a C
-sputtering time dependent X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) with synchrotron-radiation. Photon energy dependent XPS of a saturated amount of Cs doped on a C film at room temperature (RT). The energy-dependence of the apparent intensity ratio of Cs 3d and C 1s was scarce. It was found that Cs penetrated well into C
film at room temperature (RT). The energy-dependence of the apparent intensity ratio of Cs 3d and C 1s was scarce. It was found that Cs penetrated well into C , whilst CsI deposited on C
, whilst CsI deposited on C surface at RT. However, since some experimental conditions may influence Cs depth profiles, we address this issue.
surface at RT. However, since some experimental conditions may influence Cs depth profiles, we address this issue.
Terasawa, Tomoo; Taira, Takanobu*; Obata, Seiji*; Yasuda, Satoshi; Saiki, Koichiro*; Asaoka, Hidehito
no journal, ,
Since the solubility of carbon in copper is very low, monolayer graphene can be selectively grown by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) on a copper substrate. Thus, CVD growth of graphene is considered the most promising technique for the next-generation electronics. Here we report the CVD growth of graphene on gold substrates which also have the low solubility of carbon. We achieved the in-situ observation of the CVD growth of graphene on a gold foil by radiation-mode optical microscopy (Rad-OM). Figure shows the Rad-OM images of a gold foil at the growth time of 15, 30, and 40 min at 900 C under Ar, H
C under Ar, H , and CH
, and CH gas flow at 240, 8, and 5 sccm, respectively. The bright islands, corresponding to graphene confirmed by Raman spectroscopy, appeared between two trenches of the gold foil and grew parallel to the trenches. We will discuss the growth kinetics of graphene on gold, on the basis of the in-situ Rad-OM observation.
gas flow at 240, 8, and 5 sccm, respectively. The bright islands, corresponding to graphene confirmed by Raman spectroscopy, appeared between two trenches of the gold foil and grew parallel to the trenches. We will discuss the growth kinetics of graphene on gold, on the basis of the in-situ Rad-OM observation.